Learning Modules Hide
Hide
- Chapter 1: Introduction to the Commodities Market
- Chapter 2: Understand Commodity Market Ecosystem in Detail
- Chapter 3: Understand the Working of Commodity Derivatives
- Chapter 4: Understand the Commodity Indices in Detail
- Chapter 5: Free Commodity Trading Course on Clearing and Settlement Process
- Chapter 6: Learn Risk Management for Commodity Derivatives
- Chapter 7: Understand Gold and Silver Bullion in Detail – Part 1
- Chapter 8: Bullions (Gold and Silver) – Part 2
- Chapter 9: Understand Crude Oil and Natural Gas in Detail – Part 1
- Chapter 10: Understand Crude Oil and Natural Gas in Detail – Part 2
- Chapter 11: Introduction to Base Metals
- Chapter 12: Understand Base Metals Derivatives Trading in India
- Chapter 13: Introduction to Agricultural Commodities
- Chapter 14: Understand the Uses of Commodity Derivatives
- Chapter 15: Learn Non-directional Trading Strategies in Commodities
- Chapter 16: Understand Legal and Regulatory Environment of Commodity Derivatives
Chapter 2: Understand Commodity Market Ecosystem in Detail
For the smooth functioning of any organisation, institution, or establishment, different departments need to work in cohesion to achieve common objectives. Take a look at any organisation in your locality or the company you work for -- departments such as marketing, sales, operations, research & development as well as finance and accounts work together in achieving growth for the organisation as well as generating turnover and profits.
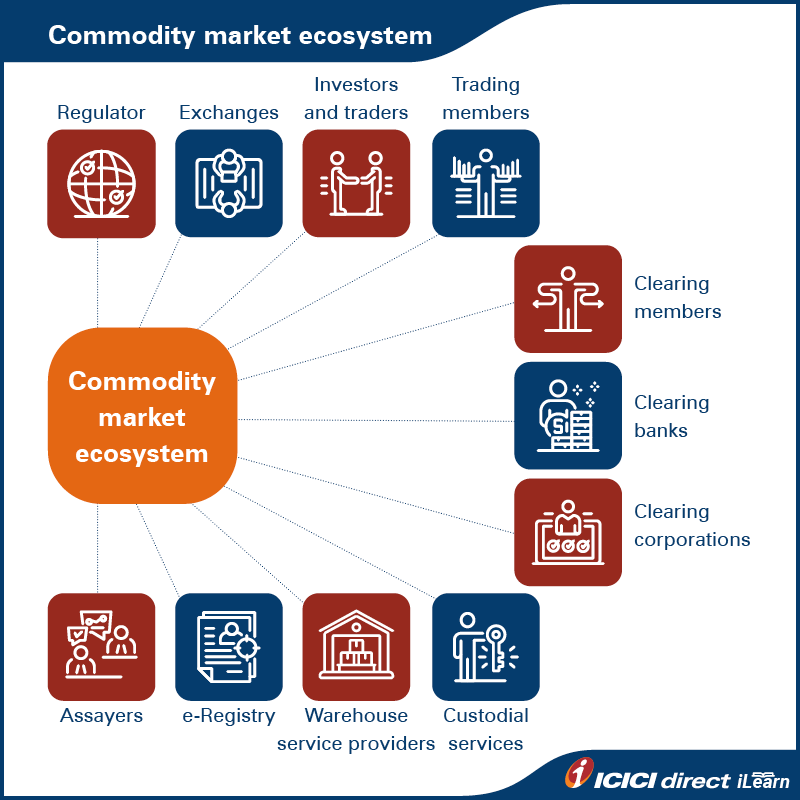
Likewise, for the smooth functioning of the commodity market, there are set of market participants who provide seamless trading experiences to buyers and sellers.
Participants in commodity derivatives market
Let us look at market participants in the commodity derivatives market:
- Regulator - SEBI
- Commodity exchanges - MCX, NCDEX, ICEX, NSE and BSE
- Investors/Traders - Traders, Hedgers and Arbitrageurs
- Market Intermediaries - Trading members, Clearing members, Warehouse service providers, Clearing banks, Assayers, Clearing corporations
Let us get to know more about these participants in detail.
1. Regulator: Each business or system is governed by a set of rules and regulations framed by the regulator. If you have a bank account, your deposits and borrowings are governed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) through a set rules and regulations that it enforces. Any violation of these rules and regulations attracts severe punishment for the defaulting party.
Likewise, the commodity market is also governed by the financial market regulator i.e., the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) Earlier, the Indian commodity derivatives market was regulated by the Forward Markets Commission (FMC), which was merged into SEBI on 28 September 2015.
This regulator’s role is to guarantee that fraud is avoided and, if it does occur, then it must be thoroughly probed. They contribute to the efficiency and transparency of markets. Also, they make sure that investors like you are treated properly and honestly.
2. Commodity exchanges: Commodity exchanges provide a trading platform where buyers and sellers are allowed to trade. These exchanges facilitate the transaction of commodities between registered brokers and investors/traders. These exchanges also design products for trading in consultation with various stakeholders within the industry. As on April, 2022, there are five functional national commodity exchanges -- Multi Commodity Exchange of India (MCX), National Commodity and Derivatives Exchange (NCDEX), Indian Commodity Exchange (ICEX), National Stock Exchange (NSE) and Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE).
|
Did you know? Multi Commodity Exchange of India (MCX) is the largest commodity exchange in India with a market share of 94% in terms of the value of commodity Futures Contracts traded. *As per data from Financial Year (FY) 2021-22 |
3. Investors/Traders: Investors/Traders in the commodity derivatives market are classified into three categories:
- Traders: As a trader, you will be taking a position in the commodity derivatives to gain profits from price fluctuations. You will get an extra leverage i.e., you can increase both potential gains and potential losses in a speculative position.
- Hedgers: If you are hedger, you will have physical exposure to the underlying commodity and will carry price risk. Hence, Futures and Options will help you mitigate this price risk through hedging in the commodity that you are exposed to.
- Arbitrageurs: As an arbitrageur, you always find opportunities of price discrepancy in two different markets. Hence, you will buy an undervalued commodity in one market and sell it in the market where it is attracting higher prices.
4. Market intermediaries: Market intermediaries play a vital role in the success of the commodity derivatives market by providing a level-playing field for buyers and sellers. Following are the different types of market intermediaries:
- Trading members
- Clearing members
- Clearing corporations
- Clearing banks
- Custodial services
- Warehouse service providers
- e-Registry
- Assayers
Since you are going to trade in the commodity market, it is very essential that you should know the roles and responsibilities of these intermediaries.
a. Trading members: A commodity exchange member, often known as a trading member, provides commodity trading services to investors. These traders could be individuals or partnership firms and companies, if they meet the membership criteria.
b. Clearing members: These members clear and settle the trade executed by trading members with the help of clearing corporations and clearing banks.
c. Clearing corporations: These corporations perform the role of a mediator between two parties through exchange of commodity contracts and funds between buyers and sellers. These entities help in elimination of counter party risks.
d. Clearing banks: A clearing bank serves as the intermediary between clearing corporations and clearing members. To settle cash and other responsibilities to clearing corporations, each clearing member must hold an account with a clearing bank.
e. Custodial services: These organisations act as a repository for electronically maintaining records of warehouse goods, which can also be used for clearing and settlement of trades on exchanges.
f. Warehouse service providers: Commodity derivatives are distinct from equity derivatives because commodities can be deliverable contracts. Upon expiry of the contract, the exchange of physical commodities takes place between buyers and sellers. Hence, warehouse service providers offer a warehousing system for the storage of commodities.
|
Did you know? All exchange empanelled warehouses come under the regulation of Warehousing Development and Regulatory Authority (WDRA). |
g. e-Registry: An e-registry keeps electronic records of ownership of goods against Negotiable Warehouse Receipts (NWRs) and Warehouse Receipts (WRs) and facilitates the electronic transfer of ownership of those products. The functions of the e-Registry include: Maintaining the original depositor's identification; checking warehouse charges/stocks online; consolidating and separating products into deliverable lots according to contract specifications.
h. Assayers: The quality of the commodity is a key component in the exchange of commodities between buyers and sellers. For a manufactured commodity, the standard quality is maintained during the production process. However, the quality of agri commodities varies a lot due to various natural factors. Hence, assayers play an important role in assuring delivery of quality goods to buyers.
Summary
- For success of the commodity market, it is necessary that all key players work in coordination and cooperation with each other.
- The commodity market distinguishes itself from the equity market because of the exchange of physical goods upon expiry of contracts.
- Participants in commodity trading include the regulator, exchanges, investors/traders, market intermediaries such as trading members, clearing members, clearing corporations, clearing banks, warehouse service providers, assayers, etc.
- The commodity ecosystem consists of more participants than that of equities and other asset classes.
In the next chapter, you will gain more knowledge about trading systems in the exchange, trading rules, selection criteria for commodities chosen for trading as well as order types.
 Top Mutual Funds
Top Mutual Funds






COMMENT (0)