Learning Modules Hide
Hide
- Chapter 1: Introduction to the Commodities Market
- Chapter 2: Understand Commodity Market Ecosystem in Detail
- Chapter 3: Understand the Working of Commodity Derivatives
- Chapter 4: Understand the Commodity Indices in Detail
- Chapter 5: Free Commodity Trading Course on Clearing and Settlement Process
- Chapter 6: Learn Risk Management for Commodity Derivatives
- Chapter 7: Understand Gold and Silver Bullion in Detail – Part 1
- Chapter 8: Bullions (Gold and Silver) – Part 2
- Chapter 9: Understand Crude Oil and Natural Gas in Detail – Part 1
- Chapter 10: Understand Crude Oil and Natural Gas in Detail – Part 2
- Chapter 11: Introduction to Base Metals
- Chapter 12: Understand Base Metals Derivatives Trading in India
- Chapter 13: Introduction to Agricultural Commodities
- Chapter 14: Understand the Uses of Commodity Derivatives
- Chapter 15: Learn Non-directional Trading Strategies in Commodities
- Chapter 16: Understand Legal and Regulatory Environment of Commodity Derivatives
Chapter 3: Understand the Working of Commodity Derivatives
Let us assume that you have decided to buy a smartphone and are thinking about buying an Android or iOS device. Before making a purchase decision, you will carry out a thorough research about its features and functions. While checking the functionality, you will also consider aspects such as battery life, storage, camera, technology used, display etc. Each of these smartphones have their own features and work with a certain kind of technology. Likewise, the commodity derivatives market also has its own trading system, trading rules and order types.
Let us start with the exchange trading system.
Trading system in the exchanges
As in the case of the equity market, the commodity derivatives exchange also offers a nationwide online screen-based trading system. As an investor or trader, you will place your buy and sell orders through this screen-based trading system. Your buy or sell order gets executed as soon as the order matches with the counterparty.
You might be wondering if your order will be executed on priority? Order execution takes place on a price-time priority, which means that all orders that are received in the system are sorted on a best price basis. Orders are first sorted on their received prices and then on a time priority basis. For an efficient trading system, the highest price buy orders and lowest price sell orders are matched first and the same logic follows.
The best part of the screen-based trading system is that your trade execution happens instantaneously irrespective of your geographical location. When your order is executed, an order number is generated ensuring the accuracy of your trade, and which can be traced later in case of any discrepancies. Since the entire trading happens online, you can trade using either desktops, laptops, and smartphone.
Trading rules
- As a buyer or seller of commodity Futures, you are required to pay an initial margin upfront
- Your position is exposed to mark to market, if kept open.
- Since commodity Futures are deliverable contracts, you might end up either giving or taking delivery of the commodity if the same is not squared off before the expiry of the contract.
- You can square off the position either on the same day of trade or carry it till the expiry of the contract.
- The margins paid while taking a position will be released upon squaring of the contract.
In the screen-based trading system, either you or your broker place an order manually through the system. However, in the present era of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), there is another method of trading in the commodities market i.e., Algorithm Trading.
In algorithm trading, which is also known as High Frequency Trading (HFT), the computer algorithm automatically determines the order and trade execution in terms of price, quantity, and timing with limited or no human intervention at all. Algorithm trading employs a defined set of instructions on timing, price, quantity, or any mathematical model for placing orders at a faster pace and with higher frequency. Algorithm trading is permitted in commodity exchanges subject to broad SEBI guidelines dated 27 September 2016.
Selection criteria of commodities for trading on derivatives exchanges
Commodities listed on commodity exchanges have to get an approval from the regulator i.e., SEBI. Any modification/cancellation in the schedule of SEBI-approved contracts, for those contracts which are yet to be traded, require SEBI approval. SEBI has selected 91 commodities as notified commodities on which Futures trading is permitted.
A commodity exchange will introduce a commodity after considering key factors such as demand for the commodity's introduction from market participants (such as producers, processors, consumers, and traders), demand and supply dynamics, price volatility, inventory levels, stock utilisation, price elasticity, commodity market liquidity, commodity production, political sensitivity, homogeneous nature, commodity durability/expiry period, storability, government regulation and control, etc.
A commodity must have the following properties in order to be appropriate for Futures trading:
- The commodity must have appropriate demand and supply conditions, i.e., a big volume and marketable surplus.
- Prices should be variable enough to warrant the use of derivatives for hedging. As a result, hedging facilities would be in high demand.
- Nil or lower government restrictions on the commodity's supply, distribution, and prices should not have a significant impact on the commodity's supply, distribution, or prices.
- The commodity should be homogeneous, or it should be feasible to specify a standard for it, as standardised contracts are required by commodity exchanges.
- The product must be storable.
Contract specifications for commodity derivatives contracts
Since the Futures Contract is an improved version of a Forwards Contract, the exchange standardises contract specifications in order to make it a unique product for all market participants such as traders, hedgers, and arbitrageurs. The terms of trade in the form of quantity, price quotation, delivery centre, tick size, daily price limit, delivery mechanism, quality parameters, and settlement of contracts are mentioned in the contact specification. This ensures that you, the investor, get all relevant information about the commodity before investing.
Order types and conditions
To buy or sell commodity Futures on a commodity exchange, as a trader, you are required to place an order specifying buy or sell; the number of lots; expiry month and price conditions. Since trade execution happens on a price and time priority basis, you can place the following types of orders on the trading platform.
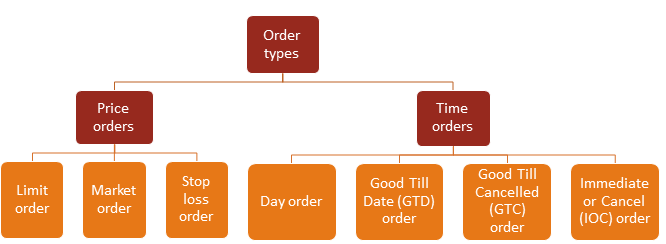
I.
Orders based on price
a. Limit order: In this order type, you will specify the price at which your trade is to be executed. If you are buying a commodity contract, you will place the limit order at a price below the current market price and vice versa. For example, if gold is trading at Rs. 48,000 per 10 grams, then as a buyer, you will place a limit order at Rs. 47,900 per 10 grams and vice versa.
b. Market order: This is another price order type where your order will be executed at the market price. When you are placing a market order to buy a particular commodity, your order will be executed at the best ask price at the time of placing the order and vice versa.
c. Stop loss order: This type of order can be placed after the execution of your trade. The main purpose of this type of order is to limit your loss if the market moves in the opposite direction of your trade. For example, let us assume you have bought gold at Rs. 48,000 per 10 grams with an expectation that the price will rise and you will make a profit. But due to certain factors, the price of gold starts falling. Hence, in order to limit your losses, you can place a stop loss order at Rs. 46,850 per 10 grams so that your position will be squared off at Rs. 46,850 per 10 grams. Stop loss orders are extremely helpful to mitigate the risk of unlimited losses during times of high volatility.
II.
Orders based on time
a. Day order: When you select the day order in the system, these orders have to be executed on the same day of placing the order. If the order doesn’t get executed on the same day, your pending order will be terminated from the system.
b. Good Till Date (GTD) order: Under Good Till Date (GTD), you can specify a date in the system and your order will be alive till that date. If the order is not executed till that date, it is terminated from the system.
c. Good Till Cancelled (GTC) order: When you place a Good Till Cancelled (GTC) order, the order will remain in the system till its execution or cancellation, whichever is earlier.
d. Immediate or Cancel (IOC) order: This is an order requiring all or part of the order to be executed immediately, after the order is placed. Any lots not executed immediately are automatically cancelled.
Tracking commodity Futures and Options prices
Commodity exchange market’s watch window displays real-time market data for commodity derivatives contracts, such as the best buy/best sell price and quantity, the last traded price, the percentage change, and the total number of buyers and sellers. The data is updated in real time on the internet. The market watch window allows investors to monitor market information of contracts, sort them in ascending/descending order, and create/modify their positions.
Summary
- Commodity exchanges provide a nationwide online trading platform making your trading experience smooth and seamless.
- Commodity exchanges desirous of launching a Futures contract have to take approval from SEBI by filling in a detailed contract specification mentioning all parameters of the trade.
- Orders can be placed based on price and time conditions.
- Contract specifications provide a detailed product note for investors.
Now that you've got a good overview of the commodity market, let's get acquainted with the commodity indices and futures in the next chapter.

 Top Mutual Funds
Top Mutual Funds





COMMENT (0)