Learning Modules Hide
Hide
- Chapter 1: Basics of Derivatives
- Chapter 2: Futures and Forwards: Know the basics – Part 1
- Chapter 3: Futures and Forwards: Know the basics – Part 2
- Chapter 4: A Complete Guide to Futures Trading
- Chapter 5: Futures Terminology
- Chapter 6 – Futures Trading – Part 1
- Chapter 7 – Futures Trading – Part 2
- Chapter 8: Understand Advanced Concepts in Futures
- Chapter 9: Participants in the Futures Market
- Chapter 1: Introduction to Derivatives
- Chapter 2: Introduction to Options
- Chapter 3: An Options Trading Course for Option Trading Terminology
- Chapter 4: All About Options Trading Call Buyer
- Chapter 5: All About Short Call in Options Trading
- Chapter 6: Learn Options Trading: Long Put (Put Buyer)
- Chapter 7: Learn Options Trading: Short Put (Put Seller)
- Chapter 8: Options Summary
- Chapter 9: Learn Advanced Concepts in Options Trading – Part 1
- Chapter 10: Learn Advanced Concepts in Options – Part 2
- Chapter 11: Learn Option Greeks – Part 1
- Chapter 12: Option Greeks – Part 2
- Chapter 13: Option Greeks – Part 3
- Chapter 1: Learn Types of Option Strategies
- Chapter 2: All About Bull Call Spread
- Chapter 3: All About Bull Put Spread
- Chapter 4: Covered Call
- Chapter 5: Bear Call Spread
- Chapter 6: Understand Bear Put Spread Option Strategy
- Chapter 7: Learn about Covered Put
- Chapter 8: Understand Long Call Butterfly in Detail
- Chapter 9: Understand Short Straddle Strategy in Detail
- Chapter 10: Understand Short Strangle Option Strategy in Detail
- Chapter 11: Understand Iron Condor Options Trading Strategy
- Chapter 12: A Comprehensive Guide to Long Straddle
- Chapter 13: Understand Long Strangle Option Strategy in Detail
- Chapter 14: Understand Short Call Butterfly Option Trading Strategy
- Chapter 15: Understanding Protective Put Strategy
- Chapter 16: Protective Call
- Chapter 17: Delta Hedging Strategy: A Complete Guide for Beginners
Chapter 14: Understand Short Call Butterfly Option Trading Strategy
Abhinav’s new manager tells him that she is expecting huge volatility in the price of a stock, ABC Ltd., but has a neutral view on the direction. She asks Abhinav to pick out an Options strategy that would be beneficial in this situation. After some research, Abhinav suggests Short Call Butterfly.
What is Short Call Butterfly
A Short Call Butterfly is a three-legged Options strategy that involves selling one ITM Call Option, buying two ATM Call Options of the same strike and selling one OTM Call Option, where the three strike prices have an equal difference.
This strategy is used when the trader is neutral on the direction of the market, but is very bullish on the movement of the prices of the underlying. Since Simran believes that there will be huge volatility in the prices of the underlying, either on the upside or downside, she acknowledges that Abhinav’s suggestion is a good one.
- This strategy will give maximum profit when the spot prices reach either the lower or higher strike prices of the Call Options.
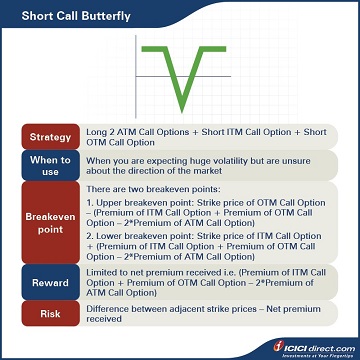
Strategy: Long 2 ATM Call Options (Leg 1) + Short ITM Call Option (Leg 2) + Short OTM Call Option (Leg 3)
When to use: When you are expecting huge volatility but are unsure about the direction of the market
Breakeven: There are two breakeven points:
1. Upper breakeven point: Strike price of OTM Call Option – (Premium of ITM Call Option + Premium of OTM Call Option – Premium of ATM Call Option)
2. Lower breakeven point: Strike price of ITM Call Option + (Premium of ITM Call Option + Premium of OTM Call Option – Premium of ATM Call Option)
Maximum profit: Limited to net premium received i.e. (Premium of ITM Call Option + Premium of OTM Call Option – Premium of ATM Call Option)
Maximum risk: Difference between adjacent strike prices – Net premium received
|
Did you know? A Short Call Butterfly is a great strategy to employ when you are confident that an underlying security may move in either direction. This is an advanced strategy that limits the risk to reward ratio. |
Let’s understand the Short Call Butterfly strategy with an example:
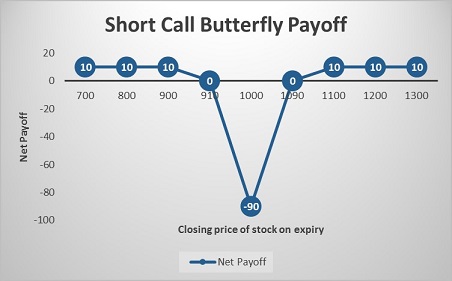
Assume that the spot price of ABC Ltd. is Rs. 1,000. Abhinav sells an ABC Ltd. ITM Call of strike price Rs. 900 at Rs. 140, sells an OTM Call of strike price Rs. 1,100 at Rs. 30, and buys 2 ATM Call Options of strike price Rs. 1,000 at Rs. 80. He receives a total premium of Rs. 140 + Rs. 30 – Rs. 2*80 = Rs. 10, and this will be the maximum profit.
Let’s take a look at the cash flow in various scenarios:

If the stock closes at Rs. 800 on expiry: All the three legs expire OTM Let’s understand the payoff in various scenarios. It will give you a fair idea of how we have arrived at the above values.
Leg 1: Premium paid on the two ATM Call Options of strike price Rs. 1000 = 2*80 = Rs. 160
Premium received on the two ATM Call Options of strike price Rs. 1000 = 2* Max {0, (Spot price – Strike price)} = 2* Max {0, (800 – 1000)} = 2*Max (0, – 200) = 0
So, the payoff from the two ATM Call Options = Premium received – Premium paid = 0 – 160 = –Rs. 160
Leg 2: Premium received on the ITM Call Option of strike price Rs. 900 = Rs. 140
Premium paid on ITM Call Option of strike price Rs. 900 at expiry = Max {0, (Spot price – Strike price)} = Max {0, (800 – 900)} = Max (0, – 100) = 0
So, the payoff from the ITM Call Option = Premium received – Premium paid = 140 – 0 = Rs. 140
Leg 3: Premium received on the OTM Call Option of strike price Rs.1100 = Rs. 30
Premium paid on OTM Call Option of strike price Rs. 1100 at expiry = Max {0, (Spot price – Strike price)} = Max {0, (800 – 1100)} = Max (0, – 300) = 0
So, the Payoff from the OTM Call Option = Premium received – Premium paid = 30 – 0 = Rs. 30
Net Payoff = Payoff from two ATM Call Options + Payoff from ITM Call Option + Payoff from OTM Call Option = (– 160) + 140 + 30 = Rs. 10
If the stock closes at Rs. 1090 on expiry: Leg 1 and leg 2 expire ITM while leg 3 expires OTM
Leg 1: Premium paid on the two ATM Call Options of strike price Rs. 1000 = 2*80 = Rs. 160
Premium received on the two ATM Call Options of strike price Rs. 1000 = 2* Max {0, (Spot price – Strike price)} = 2* Max {0, (1090 – 1000)} = 2*Max (0, 90) = 2*90 = Rs. 180
So, the payoff from the two ATM Call Options = Premium received – Premium paid = 180 – 160 = Rs. 20
Leg 2: Premium received on the ITM Call Option of strike price Rs. 900 = Rs. 140
Premium paid on ITM Call Option of strike price Rs. 900 at expiry = Max {0, (Spot price – Strike price)} = Max {0, (1090 – 900)} = Max (0, 190) = Rs. 190
So, the payoff from the ITM Call Option = Premium received – Premium paid = 140 – 190 = – Rs. 50
Leg 3: Premium received on the OTM Call Option of strike price Rs.1100 = Rs. 30
Premium paid on the OTM Call Option of strike price Rs. 1100 at expiry = Max {0, (Spot price – Strike price)} = Max {0, (1090 – 1100)} = Max (0, – 10) = 0
So, the Payoff from the OTM Call Option = Premium received – Premium paid = 30 – 0 = Rs. 30
Net Payoff = Payoff from two ATM Call Options + Payoff from ITM Call Option + Payoff from OTM Call Option = 20 + (– 50) + 30 = 0
If the Stock closes at Rs. 1200 on expiry: All three legs expire ITM
Leg 1: Premium paid on the two ATM Call Options of strike price Rs. 1000 = 2*80 = Rs. 160
Premium received on the two ATM Call Options of strike price Rs. 1000 = 2* Max {0, (Spot price – Strike price)} = 2* Max {0, (1200 – 1000)} = 2*Max (0, 200) = 2*200 = Rs. 400
So, the payoff from the two ATM Call Options = Premium received – Premium paid = 400 – 160 = Rs. 240
Leg 2: Premium received on the ITM Call Option of strike price Rs. 900 = Rs. 140
Premium paid on ITM Call Option of strike price Rs. 900 at expiry = Max {0, (Spot price – Strike price)} = Max {0, (1200 – 900)} = Max (0, 300) = Rs. 300
So, the payoff from the ITM Call Option = Premium received – Premium paid = 140 – 300 = – Rs. 160
Leg 3: Premium received on the OTM Call Option of strike price Rs.1100 = Rs. 30
Premium paid on OTM Call Option of strike price Rs. 1100 at expiry = Max {0, (Spot price – Strike price)} = Max {0, (1200 – 1100)} = Max (0, 100) = Rs.100
So, the Payoff from the OTM Call Option = Premium received – Premium paid = 30 – 100 = – Rs. 70
Net Payoff = Payoff from two ATM Call Options + Payoff from ITM Call Option + Payoff from OTM Call Option = 240 + (– 160) + (– 70) = Rs. 10
Additional Read: What are Options? How do they work? Types and Features of Option
Summary
- A Short Call Butterfly is a three-legged Options strategy that involves selling one ITM Call Option, buying two ATM Call Options and selling one OTM Call Option where the three strike prices have an equal difference.
- This strategy is used when the trader is neutral on the direction of the market but is very bullish on the movement of the prices of the underlying.
- Breakeven: There are two breakeven points:
- Upper breakeven point: Strike price of OTM Call Option – (Premium of ITM Call Option + Premium of OTM Call Option – Premium of ATM Call Option)
- Lower breakeven point: Strike price of ITM Call Option + (Premium of ITM Call Option + Premium of OTM Call Option – Premium of ATM Call Option)
- Maximum profit: Limited to net premium received i.e. (Premium of ITM Call Option + Premium of OTM Call Option – Premium of ATM Call Option)
- Maximum risk: Difference between adjacent strike prices – Net premium received
We have just delved into the details of the Short Call Butterfly strategy. In the next chapter, we take a look at the dynamics of an Options strategy called Protective Put. As the name suggests, it protects you from loss on a long delivery position.

 Top Mutual Funds
Top Mutual Funds





COMMENT (0)