Learning Modules Hide
Hide
- Chapter 1: Basics of Derivatives
- Chapter 2: Futures and Forwards: Know the basics – Part 1
- Chapter 3: Futures and Forwards: Know the basics – Part 2
- Chapter 4: A Complete Guide to Futures Trading
- Chapter 5: Futures Terminology
- Chapter 6 – Futures Trading – Part 1
- Chapter 7 – Futures Trading – Part 2
- Chapter 8: Understand Advanced Concepts in Futures
- Chapter 9: Participants in the Futures Market
- Chapter 1: Introduction to Derivatives
- Chapter 2: Introduction to Options
- Chapter 3: An Options Trading Course for Option Trading Terminology
- Chapter 4: All About Options Trading Call Buyer
- Chapter 5: All About Short Call in Options Trading
- Chapter 6: Learn Options Trading: Long Put (Put Buyer)
- Chapter 7: Learn Options Trading: Short Put (Put Seller)
- Chapter 8: Options Summary
- Chapter 9: Learn Advanced Concepts in Options Trading – Part 1
- Chapter 10: Learn Advanced Concepts in Options – Part 2
- Chapter 11: Learn Option Greeks – Part 1
- Chapter 12: Option Greeks – Part 2
- Chapter 13: Option Greeks – Part 3
- Chapter 1: Learn Types of Option Strategies
- Chapter 2: All About Bull Call Spread
- Chapter 3: All About Bull Put Spread
- Chapter 4: Covered Call
- Chapter 5: Bear Call Spread
- Chapter 6: Understand Bear Put Spread Option Strategy
- Chapter 7: Learn about Covered Put
- Chapter 8: Understand Long Call Butterfly in Detail
- Chapter 9: Understand Short Straddle Strategy in Detail
- Chapter 10: Understand Short Strangle Option Strategy in Detail
- Chapter 11: Understand Iron Condor Options Trading Strategy
- Chapter 12: A Comprehensive Guide to Long Straddle
- Chapter 13: Understand Long Strangle Option Strategy in Detail
- Chapter 14: Understand Short Call Butterfly Option Trading Strategy
- Chapter 15: Understanding Protective Put Strategy
- Chapter 16: Protective Call
- Chapter 17: Delta Hedging Strategy: A Complete Guide for Beginners
Chapter 4: Covered Call
Abhinav now knows what Bull Call Spreads and Bull Put Spreads are. Both are multi-leg Options strategies used when an investor is bullish about the market. Abhinav is still eager to learn more, and continues to question his manager on the subject. His manager then goes on to explain the concept of another multi-leg Options strategy that can be used when the investor is bullish: The Covered Call. It applies to situations wherein you have a bullish view over the medium to long-term, but are just mildly bullish in the near term. However, you still want to earn that extra buck in this time span. In a Covered Call, the profit an investor can make is limited, and the protection offered will also not be much in the event that the price of the stock drops.
Looking at the Covered Call
In a Covered Call, the investor who sells Call Options holds the same portion of the underlying security. In other words, it can be defined as a strategy in which you can short a Call Option on the stock and simultaneously hold the same underlying.
As mentioned earlier, in a Covered Call, you buy the underlying with a bullish view over the medium to long-term, but are mildly bullish about the near term. Here, you can write the OTM Call Option at the strike price at which you target selling your underlying.
In this manner, you can earn extra income in the form of the premium received from selling the Call Option. If the spot price remains below the strike price, the Option buyer will not exercise the Option and you can retain the premium amount. The Call Option used in this strategy is normally OTM, which reduces the probability of it being exercised. Hence, you earn extra income in the near term.
- The maximum risk in this strategy is equal to the difference between the stock price and the premium received.
- The upside is limited to the amount equal to the difference between the strike price and purchase price of the stock plus the premium received.
Strategy: Buy the stock in the spot market + Sell the OTM stock Call Option
When to use: When you have a bullish view over the medium to long-term but mildly bullish in the near-term and still want to earn extra income in the near-term
Breakeven: Purchase price of the stock – Premium received from shorting Call Option
Maximum profit: Call strike price – Purchase price of the stock + Call premium
Maximum risk: Purchase price of the stock – Call premium
Let’s understand this strategy with an example:
Abhinav buys shares of ABC Ltd. for Rs. 1,000 and simultaneously sold an ABC Ltd. Call Option at a strike price of Rs. 1,100, available in the market at Rs. 50. Abhinav believes that the price of ABC Ltd. will not rise above Rs. 1,100. However, in case it does, he will still make a profit of Rs. 100 from his Call Option and can exit from the stock.
He received a premium of Rs. 50 for selling the Call. Thus, net outflow is (Rs. 1000 – Rs. 50) = Rs. 950. Using this strategy, Abhinav would have effectively reduced the cost of buying the stock.
If the stock price stays at or below Rs. 1,100, the Call Option will not get exercised and he can retain the premium of Rs. 50, which becomes extra income.
If the stock price goes above Rs. 1,100, the Call Option will get exercised by the Call buyer.
Here is a glimpse of the cash flow in various scenarios:
|
Closing price of ABC Ltd. on expiry (Rs.) |
Payoff from spot position (A) (Rs.) |
Payoff from OTM Call Option (B) (Rs.) |
Net payoff (A+B) (Rs.) |
|
800 |
– 200 |
50 |
– 150 |
|
900 |
– 100 |
50 |
– 50 |
|
950 |
– 50 |
50 |
0 |
|
1000 |
0 |
50 |
50 |
|
1100 |
100 |
50 |
150 |
|
1200 |
200 |
– 50 |
150 |
Let us understand the payoff in these scenarios, as it will give you a fair idea of how we have arrived at the above values.
If the stock closes at Rs. 800 on expiry: The sold Call Option will expire OTM
The purchase price of the stock = Rs. 1000
The selling price of the stock on expiry = Rs. 800
So, the payoff from the spot position = Selling price – Purchase price = 800 – 1000 = – Rs. 200
Premium received on the OTM Call Option of strike price Rs. 1100 = Rs. 50
Premium paid on OTM Call Option of strike price Rs. 1100 at expiry = Max {0, (Spot price – Strike price)} = Max {0, (800 – 1100)} = Max (0, – 300) = 0
So, the payoff from the OTM Call Option = Premium received – Premium paid = 50 – 0 = Rs. 50
Net payoff = Payoff from the spot position + Payoff from OTM Call Option = (– 200) + 50 = – Rs. 150
If stock closes at Rs. 950 on expiry: The sold Call Option will expire OTM
The purchase price of the stock = Rs. 1000
The selling price of the stock on expiry = Rs. 950
So, the payoff from the spot position = Selling price – Purchase price = Rs 950 – Rs 1000 = – Rs. 50
Premium received on the OTM Call Option of strike price Rs.1100 = Rs. 50
Premium paid on OTM Call Option of strike price Rs. 1100 at expiry = Max {0, (Spot price – Strike price)} = Max {0, (950 – 1100)} = Max (0, – 150) = 0
So, the payoff from the OTM Call Option = Premium received – Premium paid = 50 – 0 = Rs. 50
Net payoff = Payoff from the spot position + Payoff from the OTM Call Option = (– 50) + 50 = 0
If the stock closes at Rs. 1200 on expiry: The sold Call Option with expire ITM
The purchase price of the stock = Rs. 1000
The selling price of the stock on expiry = Rs. 1200
So, the payoff from the spot position = Selling price – Purchase price = 1200 – 1000 = Rs. 200
Premium received on the OTM Call Option of strike price Rs.1100 = Rs.50
Premium paid on OTM Call Option of strike price Rs. 1100 at expiry = Max {0, (Spot price – Strike price)} = Max {0, (1200 – 1100)} = Max (0, 100) = Rs. 100
So, the payoff from the OTM Call Option = Premium received – Premium paid = 50 – 100 = – Rs. 50
Net payoff = Payoff from the spot position + Payoff from the OTM Call Option = 200 + (– 50) = Rs. 150
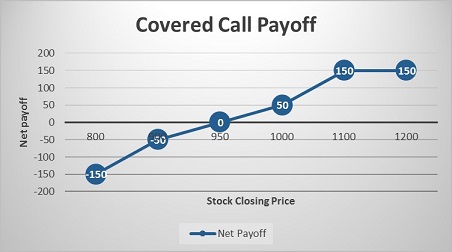
|
Did you know? There is an important precaution to take with Covered Calls: Never use this strategy as a single-leg Options strategy. For instance, if you see the price of a stock going up, refrain from booking profits on the cash market position and holding the short Call. You lose your hedged position here and losses can mount steeply. |
This brings us to the end of multi-leg Options strategies that can be used when an investor has a bullish view of the market. However, Abhinav’s curiosity and thirst for knowledge has not been satiated, and he wants to understand more: What if someone is bearish? What are the options (pun intended) available then?
His manager highlights there are three strategies available if someone has a bearish view:
- Bear Call Spread
- Bear Put Spread
- Covered Put
Summary

- A Covered Call is a strategy in which you can short a Call Option on the stock, while simultaneously holding the same underlying.
- Timing: In this case, you buy the underlying with a bullish view over the medium to long-term, but are mildly bullish in the near-term.
- Breakeven: Purchase price of the stock – Premium received for shorting Call Option
- Maximum profit: Call strike price – Purchase price of the stock + Call Premium
- Maximum risk: Purchase price of the stock – Call Premium
Additional Read: What are Options? How do they work? Types and Features of Options
As you have seen till now, there are more ways to make money than just investing or trading in stocks directly. Derivatives offer a host of alternate ways in which income can be generated, so let’s read the forthcoming chapters to discover more methods to rake in the moolah!
Disclaimer:
ICICI Securities Ltd. ( I-Sec). Registered office of I-Sec is at ICICI Securities Ltd. - ICICI Venture House, Appasaheb Marathe Marg, Prabhadevi, Mumbai - 400 025, India, Tel No : 022 - 2288 2460, 022 - 2288 2470. The contents herein above shall not be considered as an invitation or persuasion to trade or invest. I-Sec and affiliates accept no liabilities for any loss or damage of any kind arising out of any actions taken in reliance thereon. The contents herein above are solely for informational purpose and may not be used or considered as an offer document or solicitation of offer to buy or sell or subscribe for securities or other financial instruments or any other product. Investments in securities market are subject to market risks, read all the related documents carefully before investing. The contents herein mentioned are solely for informational and educational purpose.

 Top Mutual Funds
Top Mutual Funds





COMMENT (0)