Learning Modules Hide
Hide
- Chapter 1: Basics of Derivatives
- Chapter 2: Futures and Forwards: Know the basics – Part 1
- Chapter 3: Futures and Forwards: Know the basics – Part 2
- Chapter 4: A Complete Guide to Futures Trading
- Chapter 5: Futures Terminology
- Chapter 6 – Futures Trading – Part 1
- Chapter 7 – Futures Trading – Part 2
- Chapter 8: Understand Advanced Concepts in Futures
- Chapter 9: Participants in the Futures Market
- Chapter 1: Introduction to Derivatives
- Chapter 2: Introduction to Options
- Chapter 3: An Options Trading Course for Option Trading Terminology
- Chapter 4: All About Options Trading Call Buyer
- Chapter 5: All About Short Call in Options Trading
- Chapter 6: Learn Options Trading: Long Put (Put Buyer)
- Chapter 7: Learn Options Trading: Short Put (Put Seller)
- Chapter 8: Options Summary
- Chapter 9: Learn Advanced Concepts in Options Trading – Part 1
- Chapter 10: Learn Advanced Concepts in Options – Part 2
- Chapter 11: Learn Option Greeks – Part 1
- Chapter 12: Option Greeks – Part 2
- Chapter 13: Option Greeks – Part 3
- Chapter 1: Learn Types of Option Strategies
- Chapter 2: All About Bull Call Spread
- Chapter 3: All About Bull Put Spread
- Chapter 4: Covered Call
- Chapter 5: Bear Call Spread
- Chapter 6: Understand Bear Put Spread Option Strategy
- Chapter 7: Learn about Covered Put
- Chapter 8: Understand Long Call Butterfly in Detail
- Chapter 9: Understand Short Straddle Strategy in Detail
- Chapter 10: Understand Short Strangle Option Strategy in Detail
- Chapter 11: Understand Iron Condor Options Trading Strategy
- Chapter 12: A Comprehensive Guide to Long Straddle
- Chapter 13: Understand Long Strangle Option Strategy in Detail
- Chapter 14: Understand Short Call Butterfly Option Trading Strategy
- Chapter 15: Understanding Protective Put Strategy
- Chapter 16: Protective Call
- Chapter 17: Delta Hedging Strategy: A Complete Guide for Beginners
Chapter 6: Understand Bear Put Spread Option Strategy
Abhinav’s manager anticipates a dip in the market in the coming months, and asks him to prepare a report on Bear Put Spreads for a client. Abhinav knows that these are multi-leg Options strategies that are used when an investor has a negative or bullish outlook on the market, but his knowledge on the subject is limited. He then decides to read up on it, and let’s take a look at what he learnt.
Looking at the Bear Put Spread
When a trader is moderately bearish on the price movement of an underlying asset, he can use a Bear Put Spread strategy. This is a strategy that involves the use of two Put Options. You buy an ITM Put Option and simultaneously sell an OTM Put Option with the same expiry, underlying asset and involving the same number of Options. This way, you will have a net cash outflow at the start of trade. The premium paid will be more than that received.
|
Did you know? Bear Put Spread is also known as Debit Put Spread or Long Put Spread. |
This strategy is used when the trader is moderately bearish on the direction of prices of the underlying but wants to reduce his initial cost of long Put by getting a premium on the short Put.
- Maximum profit will be incurred when the Options are exercised with gains equal to the difference between the strike price and net premium paid at the beginning of trade.
- Maximum loss would be incurred when the Options are not exercised with losses equal to the net premium paid at the beginning of trade.
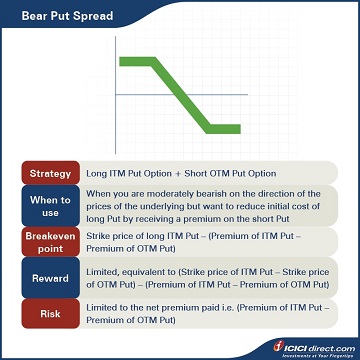
Strategy: Long ITM Put Option (Leg 1) + Short OTM Put Option (Leg 2)
When to use: When you are moderately bearish on the direction of the prices of the underlying, but want to reduce the initial cost of long Put by receiving a premium on the short Put
Breakeven: Strike price of long ITM Put – (Premium of ITM Put – Premium of OTM Put)
Maximum profit: Limited, equivalent to (Strike price of ITM Put – Strike price of OTM Put) – (Premium of ITM Put – Premium of OTM Put)
Maximum risk: Limited to the net premium paid i.e. (Premium of ITM Put – Premium of OTM Put)
Let’s understand the Bear Put Spread strategy with an example:
Assume that the spot price of ABC Ltd. is Rs. 1,000. Abhinav finds out that if he bought an ABC Ltd. ITM Put Option of strike price Rs. 1,100 at Rs. 140 and sold an OTM Put Option of strike price Rs. 800 at Rs. 20, he can limit his losses even if the price of the stock falls. He would be paying a total premium of Rs. 140 – Rs 20 = Rs. 120 and this will be the maximum loss. He will start gaining if the stock moves beyond the lower strike price, i.e. Rs. 800.
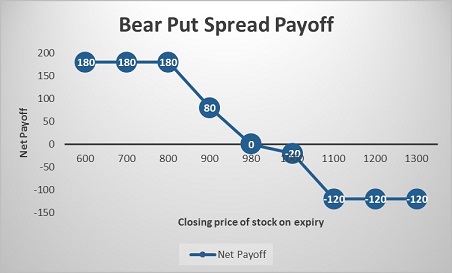
Let’s take a look at the cash flow in various scenarios:
|
Closing price of stock on expiry (Rs.) |
Payoff from ITM Put Option (A) (Rs.) |
Payoff from OTM Put Option (B) (Rs.) |
Net payoff (A+B) (Rs.) |
|
600 |
360 |
– 180 |
180 |
|
700 |
260 |
– 80 |
180 |
|
800 |
160 |
20 |
180 |
|
900 |
60 |
20 |
80 |
|
980 |
– 20 |
20 |
0 |
|
1000 |
– 40 |
20 |
– 20 |
|
1100 |
– 140 |
20 |
– 120 |
|
1200 |
– 140 |
20 |
– 120 |
|
1300 |
– 140 |
20 |
– 120 |
Let us understand the payoff in various scenarios. It will give you a fair idea of how we have arrived at the above values.
If the stock closes at Rs. 700 on expiry: Both legs expire ITM
Leg 1: Premium paid on the ITM Put Option of strike price Rs. 1100 = Rs. 140
Premium received on ITM Put Option of strike price Rs.1100 at expiry = Max {0, (Strike price – Spot price)} = Max {0, (1100 – 700)} = Max (0, 400) = Rs. 400
So, the payoff from the ITM Put Option = Premium received – Premium paid = 400 – 140 = Rs. 260
Leg 2: Premium received on the OTM Put Option of strike price Rs.800 = Rs. 20
Premium paid on OTM Put Option of strike price Rs. 800 at expiry = Max {0, (Strike price – Spot price)} = Max {0, (800 – 700)} = Max (0, 100) = Rs. 100
So, the payoff from the OTM Put Option = Premium received – Premium paid = 20 – 100 = – Rs. 80
Net payoff = Payoff from ITM Put Option + Payoff from OTM Put Option = 260 + (– 80) = Rs. 180
If the stock closes at Rs. 980 on expiry: Leg 1 expires ITM while leg 2 expires OTM
Leg 1: Premium paid on the ITM Put Option of strike price Rs. 1100 = Rs. 140
Premium received on ITM Put Option of strike price Rs. 1100 at expiry = Max {0, (Strike price – Spot price)} = Max {0, (1100 – 980)} = Max (0, 120) = Rs. 120
So, the payoff from the ITM Put Option = Premium received – Premium paid = Rs 120 – Rs 140 = – Rs. 20
Leg 2: Premium received on the OTM Put Option of strike price Rs.800 = Rs. 20
Premium paid on OTM Put Option of strike price Rs. 800 at expiry = Max {0, (Strike price – Spot price)} = Max {0, (800 – 980)} = Max (0, – 180) = 0
So, the payoff from the OTM Put Option = Premium received – Premium paid = 20 – 0 = Rs. 20
Net payoff = Payoff from ITM Put Option + Payoff from OTM Put Option = (– 20) + 20 = 0
If the stock closes at Rs. 1200 on expiry: Both legs expire OTM
Leg 1: Premium paid on the ITM Put Option of strike price Rs. 1100 = Rs. 140
Premium received on ITM Put Option of strike price Rs. 1100 at expiry = Max {0, (Strike price – Spot price)} = Max {0, (1100 – 1200)} = Max (0, – 100) = 0
So, payoff from the ITM Put Option = Premium received – Premium paid = 0 – 140 = – Rs. 140
Leg 2: Premium received on the OTM Put Option of strike price Rs. 800 = Rs. 20
Premium paid on OTM Put Option of strike price Rs. 800 at expiry = Max {0, (Strike price – Spot price)} = Max {0, (800 – 1200)} = Max (0, – 400) = 0
So, the payoff from the OTM Put Option = Premium received – Premium paid = 20 – 0 = Rs. 20
Net payoff = Payoff from ITM Put Option + Payoff from OTM Put Option = (– 140) + 20 = – Rs. 120
Summary
Additional Read: What is a Bull Market
- A Bear Put Spread is a strategy that involves the use of two Put Options. You buy an ITM Put Option and simultaneously sell an OTM Put Option with the same expiry and on the same underlying asset involving the same number of Options. This way, you will have a net cash outflow at the start of trade.
- Breakeven: Strike price of long ITM Put – (Premium of ITM Put – Premium of OTM Put)
- Maximum profit: Limited, equivalent to (Strike price of ITM Put – Strike price of OTM Put) – (Premium of ITM Put – Premium of OTM Put)
- Maximum risk: Limited to the net premium paid i.e. (Premium of ITM Put – Premium of OTM Put)
In this chapter, we have seen how Bear Put Spreads function when market sentiment is low. Let’s take a look at another strategy, ‘Covered Put’ and its functioning in the next chapter.

 Top Mutual Funds
Top Mutual Funds





COMMENT (0)