Learning Modules Hide
Hide
- Chapter 1: Basics of Derivatives
- Chapter 2: Futures and Forwards: Know the basics – Part 1
- Chapter 3: Futures and Forwards: Know the basics – Part 2
- Chapter 4: A Complete Guide to Futures Trading
- Chapter 5: Futures Terminology
- Chapter 6 – Futures Trading – Part 1
- Chapter 7 – Futures Trading – Part 2
- Chapter 8: Understand Advanced Concepts in Futures
- Chapter 9: Participants in the Futures Market
- Chapter 1: Introduction to Derivatives
- Chapter 2: Introduction to Options
- Chapter 3: An Options Trading Course for Option Trading Terminology
- Chapter 4: All About Options Trading Call Buyer
- Chapter 5: All About Short Call in Options Trading
- Chapter 6: Learn Options Trading: Long Put (Put Buyer)
- Chapter 7: Learn Options Trading: Short Put (Put Seller)
- Chapter 8: Options Summary
- Chapter 9: Learn Advanced Concepts in Options Trading – Part 1
- Chapter 10: Learn Advanced Concepts in Options – Part 2
- Chapter 11: Learn Option Greeks – Part 1
- Chapter 12: Option Greeks – Part 2
- Chapter 13: Option Greeks – Part 3
- Chapter 1: Learn Types of Option Strategies
- Chapter 2: All About Bull Call Spread
- Chapter 3: All About Bull Put Spread
- Chapter 4: Covered Call
- Chapter 5: Bear Call Spread
- Chapter 6: Understand Bear Put Spread Option Strategy
- Chapter 7: Learn about Covered Put
- Chapter 8: Understand Long Call Butterfly in Detail
- Chapter 9: Understand Short Straddle Strategy in Detail
- Chapter 10: Understand Short Strangle Option Strategy in Detail
- Chapter 11: Understand Iron Condor Options Trading Strategy
- Chapter 12: A Comprehensive Guide to Long Straddle
- Chapter 13: Understand Long Strangle Option Strategy in Detail
- Chapter 14: Understand Short Call Butterfly Option Trading Strategy
- Chapter 15: Understanding Protective Put Strategy
- Chapter 16: Protective Call
- Chapter 17: Delta Hedging Strategy: A Complete Guide for Beginners
Chapter 6: Learn Options Trading: Long Put (Put Buyer)
Let’s assume Deb had been extremely bearish on ABC Ltd.’s stock. His advice to Subhanshu would have been different. Instead of going short on a Call Option, he would have advised Subhanshu to enter into a long Put Option.
Let’s understand why.
Long Put
A long Put refers to buying a Put Option, i.e. the right, not the obligation, to sell the asset at a predetermined price.
A long Put position is useful when you are strongly bearish about the underlying asset. You expect a huge downside in the stock before the expiry of the contract.
|
Did you know? A long Put can also be used to hedge a long position or buying an underlying asset. In case the price of the underlying asset falls, you can exercise the Put Option to offset the loss. |
Let’s get into this with ABC Ltd.’s example.
Assume that Subhanshu has purchased ABC Ltd.’s Rs. 1,000 Put Option at a premium of Rs. 50. This means that he has purchased the right to sell ABC at Rs. 1,000 on expiry and has paid Rs. 50 to the seller as compensation for this right. In other words, Subhanshu may sell ABC Ltd. at Rs. 1,000 on the expiry of the contract. He may sell if the market price is favorable i.e. if the price falls below Rs. 1,000.
As usual, let’s explore the three ways in which this can play out:
Scenario 1: ABC Ltd. closes at Rs. 1,200 on expiry
In this case, Subhanshu would prefer not to exercise his right to sell ABC at Rs. 1,000. It means he will have to bear a net loss equal to the premium paid of Rs.50.
Subhanshu’s breakeven point in this case will be Rs. 1,000 – Rs. 50 = Rs. 950.
Alternatively, we can also calculate the profit/loss with the help of premium paid and premium received.
Premium paid = Rs. 50
Premium received on expiry (equal to intrinsic value) = Max {0, (Strike price – Spot price)} = Max {0, (1000 – 1200)} = Max (0, – 200) = 0
Net profit/loss = Premium received – Premium paid = 0 – 50 = – Rs. 50 i.e. a loss of Rs. 50
Scenario 2: ABC closes at Rs. 800 on expiry
This is where Subhanshu’s Put Option will come in handy. In this case, he would prefer to exercise his right and sell ABC at Rs. 1,000. This means a profit of Rs. 200 compared to the market price. However, remember that he has paid Rs. 50 as a premium. Therefore, the net gain will be Rs. 200 – Rs. 50 = Rs. 150.
Alternatively, we can also calculate the profit/loss with the help of premium paid and premium received.
Premium paid = Rs. 50
Premium received on expiry (equal to intrinsic value) = Max {0, (Strike price – Spot price)} = Max {0, (1000 – 800)} = Max (0, 200) = Rs. 200
Net profit/loss = Premium received – Premium paid = 200 – 50 = Rs. 150
Scenario 3: ABC closes at Rs. 950 on expiry
Even in this case, exercising the Option will be beneficial. This is because Subhanshu can sell ABC at Rs. 1,000 instead of Rs. 950. While he would make a profit of Rs. 50, this will be netted out against the premium on the Option paid. Therefore, the net profit would be Rs. 50 – Rs. 50 = 0.
As we discussed in scenario 1, the breakeven point in this case is Rs. 950, so there won’t be any profit if ABC closes at Rs. 950.
Alternatively, we can also calculate the profit/loss with the help of premium paid and premium received.
Premium paid = Rs. 50
Premium received on expiry (equal to intrinsic value) = Max {0, (Strike price – Spot price)} = Max {0, (1000 – 950)} = Max (0, 50) = Rs. 50
Net profit/loss = Premium received – Premium paid = 50 – 50 = 0
The payoff in various scenarios is listed below:
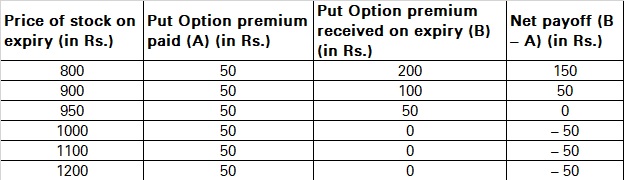
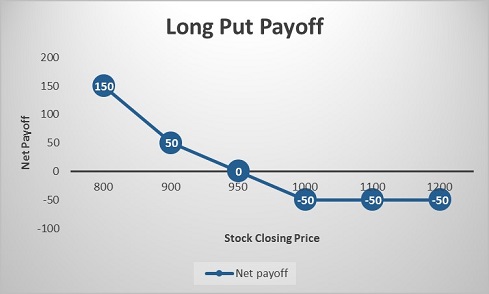
As you can see, going long on a Put Option can help you when you are extremely bearish on an asset.
- When the price of ABC Ltd. fell, Subhanshu could earn profit by exercising his right to sell at Rs. 1,000
Summary
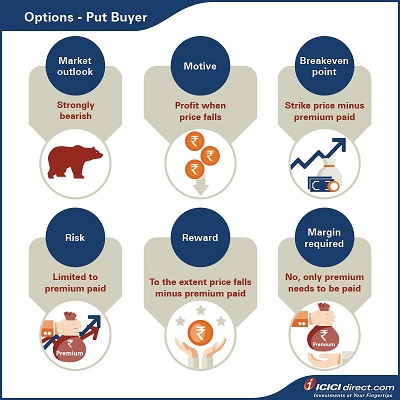
- A long Put refers to buying a Put Option, i.e. the right, not the obligation, to sell the asset at a predetermined price.
- A long Put position is useful when you are:
- Strongly bearish about an underlying asset.
- Want to hedge a long position on the asset.
- The loss in a long Put Option is limited to the premium paid.
Now that you know a long Put Option is useful when you are extremely bearish on an asset, we’ll look into when to go short on a Put Option in the upcoming chapter.

 Top Mutual Funds
Top Mutual Funds





COMMENT (0)