Learning Modules Hide
Hide
- Chapter 1: Basics of Derivatives
- Chapter 2: Futures and Forwards: Know the basics – Part 1
- Chapter 3: Futures and Forwards: Know the basics – Part 2
- Chapter 4: A Complete Guide to Futures Trading
- Chapter 5: Futures Terminology
- Chapter 6 – Futures Trading – Part 1
- Chapter 7 – Futures Trading – Part 2
- Chapter 8: Understand Advanced Concepts in Futures
- Chapter 9: Participants in the Futures Market
- Chapter 1: Introduction to Derivatives
- Chapter 2: Introduction to Options
- Chapter 3: An Options Trading Course for Option Trading Terminology
- Chapter 4: All About Options Trading Call Buyer
- Chapter 5: All About Short Call in Options Trading
- Chapter 6: Learn Options Trading: Long Put (Put Buyer)
- Chapter 7: Learn Options Trading: Short Put (Put Seller)
- Chapter 8: Options Summary
- Chapter 9: Learn Advanced Concepts in Options Trading – Part 1
- Chapter 10: Learn Advanced Concepts in Options – Part 2
- Chapter 11: Learn Option Greeks – Part 1
- Chapter 12: Option Greeks – Part 2
- Chapter 13: Option Greeks – Part 3
- Chapter 1: Learn Types of Option Strategies
- Chapter 2: All About Bull Call Spread
- Chapter 3: All About Bull Put Spread
- Chapter 4: Covered Call
- Chapter 5: Bear Call Spread
- Chapter 6: Understand Bear Put Spread Option Strategy
- Chapter 7: Learn about Covered Put
- Chapter 8: Understand Long Call Butterfly
- Chapter 9: Understand Short Straddle Strategy in Detail
- Chapter 10: Understand Short Strangle Option Strategy in Detail
- Chapter 11: Understand Iron Condor Options Trading Strategy
- Chapter 12: A Comprehensive Guide to Long Straddle
- Chapter 13: Understand Long Strangle Option Strategy in Detail
- Chapter 14: Understand Short Call Butterfly Option Trading Strategy
- Chapter 15: Understanding Protective Put Strategy
- Chapter 16: Protective Call
- Chapter 17: Delta Hedging Strategy: A Complete Guide for Beginners
Chapter 7: Learn about Covered Put
Abhinav’s manager anticipates a dip in the market in the coming months. He asks Abhinav to prepare a report on Covered Put for a client. Abhinav knows that this multi-leg Option strategy is used when an investor has a negative outlook on the market. He decides to read up more on the Covered Put.
He reads that a Covered Put is used in situations in which the trader has a negative outlook on the stock and wants to go short. Here, he can make a short stock position and also a short Put position. In this manner, he can immediately avail of some income from the premium he gets from writing the Put. Let’s take a look at this in more detail.
Looking at the Covered Put
In the event that you are mildly bearish on the market, the best strategy to adopt would be a Covered Put. This strategy will involve writing (selling) an OTM Put Option along with selling the underlying. Ideally, this strategy is well executed using stock futures due to limitation of shorting stocks by exchanges. Only intraday shorting of shares is allowed, but for the ease of understanding, the illustration here is given using underlying shares.
- As you are moderately bearish, you will not mind buying back the underlying (obligation to buy under Put Option) if the price goes down to the strike price.
- At the same time, you will make gains on your short position on the underlying as the price goes down and also on the amount of premium received on a Put Option.
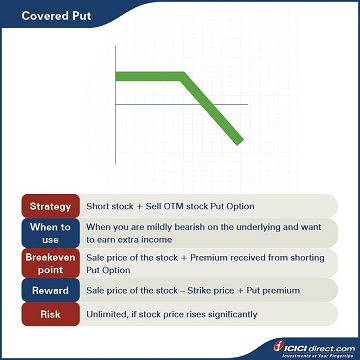
Strategy: Short stock + Sell OTM stock Put Option
When to use: When you are mildly bearish on the underlying and want to earn extra income
Breakeven: Sale price of the stock + Premium received from shorting Put Option
Maximum profit: Sale price of the stock – Strike price + Put premium
Maximum risk: Unlimited, if the stock price rises significantly
Let’s understand this strategy with an example:
Abhinav decides to sell ABC Ltd. for Rs. 1,000 and simultaneously sell an ABC Ltd. Put Option at a strike price of Rs. 900, available at Rs. 50 in the market. He believes that the price of ABC Ltd. will not fall below Rs. 900. However, in case this happens, he will buy it back.
If the stock price stays at or below Rs. 900, the Put Option will get exercised by the buyer. If the stock price goes above Rs. 1,000, the short stock position will be responsible for the losses made.
Note: This strategy is most useful only if you are mildly bearish about the prices of an underlying in the near-term.
Additional Read: What is Intraday trading? A Beginner's Guide
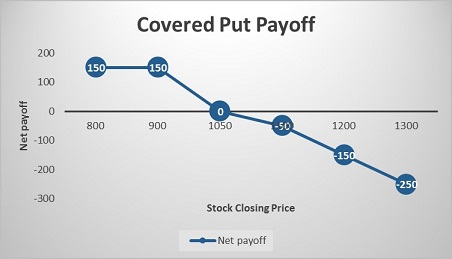
Let’s look at the cash flow in various scenarios:
|
Closing price of ABC Ltd. on expiry (Rs.) |
Payoff from spot position (A) (Rs.) |
Payoff from OTM Put Option (B) (Rs.) |
Net payoff (A+B) (Rs.) |
|
800 |
200 |
– 50 |
150 |
|
900 |
100 |
50 |
150 |
|
1050 |
– 50 |
50 |
0 |
|
1100 |
– 100 |
50 |
– 50 |
|
1200 |
– 200 |
50 |
– 150 |
|
1300 |
– 300 |
50 |
– 250 |
Let us understand the payoff in various scenarios. It will give you a fair idea of how we have arrived at the above values.
If the stock closes at Rs. 800 on expiry: The sold Put Option will expire ITM
The selling price of the stock = Rs. 1000
The purchase price of the stock on expiry = Rs. 800
So, payoff from the spot position = Selling price – Purchase price = 1000 – 800 = Rs 200
Premium received on the OTM Put Option of strike price Rs.900 = Rs. 50
Premium paid on OTM Put Option of strike price Rs. 900 at expiry = Max {0, (Strike price – Spot price)} = Max {0, (900 – 800)} = Max (0, 100) = Rs. 100
So, payoff from the OTM Call Option = Premium received – Premium paid = 50 – 100 = – Rs. 50
Net payoff = Payoff from the spot position + Payoff from OTM Call Option = 200 + (– 50) = Rs. 150
If the stock closes at Rs. 1050 on expiry: The sold Put Option will expire OTM
The selling price of the stock = Rs. 1000
The purchase price of the stock on expiry = Rs. 1050
So, payoff from the spot position = Selling price – Purchase price = 1000 – 1050 = – Rs. 50
Premium received on the OTM Put Option of strike price Rs.900 = Rs. 50
Premium paid on OTM Put Option of strike price Rs. 900 at expiry = Max {0, (Strike price – Spot price)} = Max {0, (900 – 1050)} = Max (0, – 150) = 0
So, the payoff from the OTM Call Option = Premium received – Premium paid = 50 – 0 = Rs. 50
Net payoff = Payoff from the spot position + Payoff from OTM Call Option = (– 50) + 50 = 0
If the stock closes at Rs 1200 on expiry: The sold Put Option will expire OTM
The selling price of the stock = Rs. 1000
The purchase price of the stock on expiry = Rs. 1200
So, payoff from the spot position = Selling price – Purchase price = 1000 – 1200 = – Rs. 200
Premium received on the OTM Put Option of the strike price Rs.900 = Rs. 50
Premium paid on OTM Put Option of strike price Rs. 900 at expiry = Max {0, (Strike price – Spot price)} = Max {0, (900 – 1200)} = Max (0, – 300) = 0
So, the payoff from the OTM Call Option = Premium received – Premium paid = 50 – 0 = Rs. 50
Net payoff = Payoff from the spot position + Payoff from OTM Call Option = (– 200) + 50 = – Rs. 150
Additional Read: Five key parameters to look for before buying an option
Summary
- A Covered Put strategy will involve writing an OTM Put Option along with selling the underlying.
- As you are moderately bearish, you will not mind buying back the underlying (obligation to buy under Put Option) if the price goes down to the strike price.
- At the same time, you will gain on your short position on the underlying as the price goes down and also on the amount of premium received on a Put Option.
- Breakeven: Sale price of the stock + Put premium received
- Maximum profit: Sale price of the stock – Strike price + Put premium
- Maximum risk: Unlimited, if the stock price rises significantly
After taking a look at what a Covered Put strategy entails, let us now proceed to delve into the strategy deployed when the investor/trader has a neutral view of the market.
Disclaimer:
ICICI Securities Ltd. ( I-Sec). Registered office of I-Sec is at ICICI Securities Ltd. - ICICI Venture House, Appasaheb Marathe Marg, Prabhadevi, Mumbai - 400 025, India, Tel No : 022 - 2288 2460, 022 - 2288 2470. The contents herein above shall not be considered as an invitation or persuasion to trade or invest. I-Sec and affiliates accept no liabilities for any loss or damage of any kind arising out of any actions taken in reliance thereon. The contents herein above are solely for informational purpose and may not be used or considered as an offer document or solicitation of offer to buy or sell or subscribe for securities or other financial instruments or any other product. Investments in securities market are subject to market risks, read all the related documents carefully before investing. The contents herein mentioned are solely for informational and educational purpose.

Track your application






COMMENT (0)