Tips and Best Practices for Cybersecurity
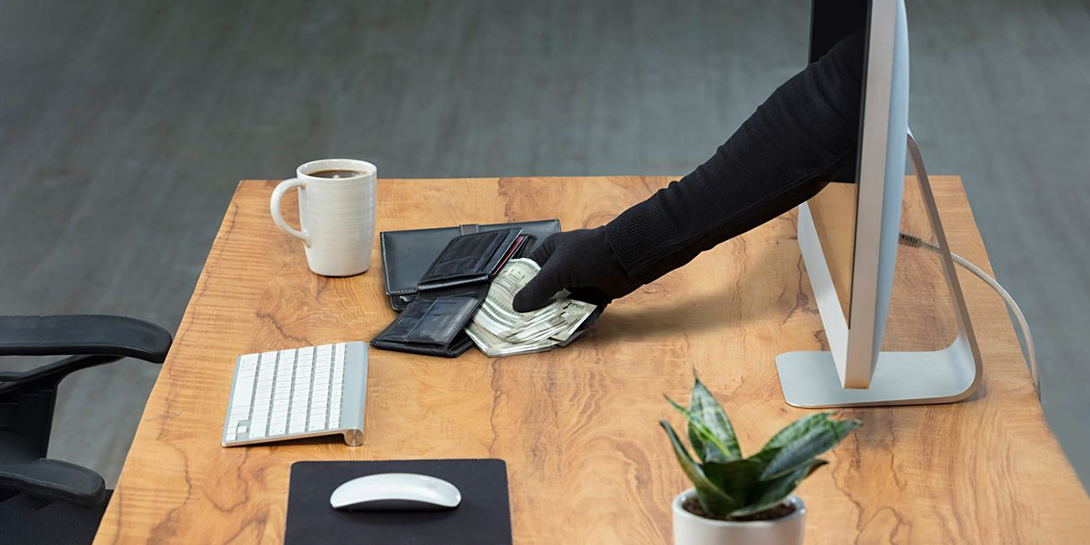

Since hacks and data breaches have become so frequent, cybersecurity has quickly become a top priority. Unfortunately, not every individual or business understands the significance of adhering to cybersecurity best practices such as creating strong passwords and activating two-factor authentication.
Cybersecurity can be challenging, especially if there is a knowledge gap. But the key is to adapt and start learning about cybersecurity. Read on to learn about some best practices everyone should incorporate into their everyday routines to keep their information safe and secure.
- Use strong and unique passwords. Don't use the same password across multiple accounts. Make passwords long, complex, alphanumeric, and difficult to guess. Consider using a password manager to generate and store strong passwords.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA). MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of identification before accessing an account. This provides an additional layer of security beyond just a password. Enable MFA on all important accounts including email, banking, social media, and work accounts.
- Keep software up to date. Maintain vigilant patch management and update programs on all devices and software. Cyber criminals exploit known vulnerabilities in outdated software. Promptly installing the latest updates and patches helps reduce these risks.
- Be wary of phishing attacks. Cybercriminals use phishing emails and fraudulent websites to trick users into revealing sensitive information. Carefully scrutinize all emails, attachments, links, and web addresses. Don't click on anything suspicious. Verify legitimacy before providing any personal or financial information.
- Practice safe web browsing. Only visit sites that use HTTPS encryption and download files only from trusted sources. Beware of fake websites. Avoid entering sensitive information on public Wi-Fi networks. Use a VPN when accessing public hotspots.
- Backup your data regularly. Keep multiple backups, both locally and in the cloud. This guarantees access to your data in case of malware infection like ransomware. Test backups regularly to verify their integrity.
- Secure your Wi-Fi network. Change the default SSID and password and use WPA2 encryption. Disable WPS and enforce a strong Wi-Fi password. Use MAC address filtering to limit connected devices. Keep your router firmware updated.
- Protect all devices. Install antivirus, anti-spyware, firewalls and other endpoint security on computers, laptops, tablets and smartphones. Scan regularly for malware. Enable auto updates to keep security tools current.
- Avoid oversharing online. Be cautious of the personal information you provide on social media and other websites. This data can aid cyber criminals in identity theft or targeted cyberattacks. Maintain online privacy and share details with discretion.
- Provide cybersecurity training. Educate all employees on cyber risks, policies, and best practices through regular training. Ensure everyone can identify threats like phishing, weak passwords, unsecured devices, and suspicious activity. Promoting cyber awareness improves organizational readiness.
- Control access with principle of least privilege. Only provide users with the bare minimum access and permissions they need to do their jobs. This limits damage if an account is compromised.
- Monitor for threats with SIEM tools. Use Security Information and Event Management software to aggregate and analyse logs from across the network. This helps identify indicators of compromise and malicious activity.
- Secure the supply chain. Vet suppliers, vendors, partners, and third-party providers for their cybersecurity practices. Require cybersecurity standards through contracts and audits. This reduces third party risks.
- Separate and segment networks. Use firewalls to isolate more sensitive networks from general business systems. Network segmentation makes lateral movement tougher for attackers.
- Dispose of devices securely. Wipe files completely and destroy storage when equipment is retired or repurposed. This prevents data recovery if devices are stolen.
Cybersecurity is an ongoing process that requires regular evaluation and adaptation to the ever-evolving threat landscape. A proactive cyber risk management strategy should aim to prevent, detect, and respond to incidents effectively. With proper planning and diligence, companies can safeguard critical assets and maintain resilience in the face of cyberattacks.
 Top Mutual Funds
Top Mutual Funds







COMMENT (0)