Learning Modules Hide
Hide
- Chapter 1: A Stock Market Guide on Equity Investment
- Chapter 2: Learn Risk & Return on Equity Investment in Detail
- Chapter 3: Learn the Basics of Stock Market Participants and Regulators
- Chapter 4: How Does the Stock Market Work?
- Chapter 5: Guide to stock market trading
- Chapter 6: Stock market investment- Part 1
- Chapter 7: Stock market investment- Part 2
- Chapter 8: What are stock market indices?
- Chapter 9: How to Calculate the Stock Exchange Index: A Stock Market Course for Beginners
- Chapter 10: IPO investing basics
- Chapter 11: Types of IPO Investors in Stock Market
- Chapter 12: IPO Process- From Merchant Banker to Company Listing
- Chapter 13: IPO investment and FPO
- Chapter 14: Important things and Advantages of IPO Investment
- Chapter 15: Corporate Actions: Meaning, Types & Examples
- Chapter 16: Bonus Issue and Rights Issue
- Chapter 17: Corporate Action Purpose and Participation Method
- Chapter 1: Stock Market Valuation- Tips and Techniques
- Chapter 2: Stock Market Valuation- Important Ratios and Terms
- Chapter 3: Types of Stocks in Share Market- Part 1
- Chapter 4 –Types of Stocks in Share Market- Part 2
- Chapter 5: Taxation on Stock Investments – Part 1
- Chapter 6 – Taxation on Stock Investments – Part 2
- Chapter 7 - Difference Between Micro & Macro Economics
- Chapter 8 – Inflation and its Impact on the Economy
- Chapter 9 - Introduction to Economic Policies – Part 1
- Chapter 10 – Introduction to Economic Policies – Part 2
- Chapter 11 – GDP and the Government Budget
- Chapter 12 – Introduction to Foreign Investments and Business Cycles
- Chapter 13 - Economic Indicators
- Chapter 14 - Behavioural Biases and Common Pitfalls in Investment – Part 1
- Chapter 15 - Behavioural Biases and Common Pitfalls in Investment – Part 2
- Chapter 16 - Behavioural Biases and Common Pitfalls in Investment – Part 3
Chapter 3: Learn the Basics of Stock Market Participants and Regulators
When you view any institution or establishment — school, college and even the company that you're working in you will see that it is a cohesive unit made up of several departments. For instance, your company has various departments including the sales, finance, human resources, marketing and others that works as a seamless organization towards success.
In the same way, the stock market also comprises a set of participants that contribute to its smooth functioning. These participants are an integral link between buyers and sellers of various securities in the securities market.
So, who are the main participants of the stock market?
Stock market participants
The main participants of the stock market include:

Let’s understand each of the them.
1. Regulator
If you are an ardent cricket fan, you would know that cricket in India is governed by the Board Council for Cricket in India (BCCI). This body is responsible in governing, administering and ensuring that all cricket regulations, including that of the Indian Premier League (IPL) are followed.
So, if something like a large sport needs to be governed and regulated, why not your investments?
In the stock market, there is a regulatory body that oversees the functioning and fairness of the stock market and the entities involved that are engaged in financial activity.
The goal of this regulator is to ensure that fraud is prevented, and if taken place is investigated thoroughly. They help keep markets efficient and transparent. And more importantly ensure that investors such as you are treated fairly and honestly.
There are various regulators for different sectors of the financial market like Ministry of Finance, RBI, SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India), IRDA (Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority), PFRDA (Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority) etc.
But for the Indian Stock Market, SEBI is the regulator.
Let’s understand the major role and functions of Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
- Protects investor’s interests in securities by conducting awareness programs
- Regulates stock market activities
- Prevents fraud or malpractices
- Helps develop the Indian Stock Market
- Grants investment advisory licenses
And that’s not all.
Consider the SEBI as a guardian of capital market participants. So, in this regard its main purpose would be to create such an environment for all participants and financial market enthusiasts to ensure that the securities market functions efficiently and works smoothly.
So, since it's a regulatory body, here are its main functionalities:
- It designs guidelines and a proper code of conduct for financial intermediaries to abide by
- It can conduct inquiries and audits of all concerned as per the SEBI Act.
- It registers and regulates various intermediaries like brokers, sub brokers, merchant bankers, etc.
- It performs and exercises powers in its control and can impose penalties for violations of the rules.
2. Stock exchanges
Let's look into the second participant of the stock market - the stock exchange.
The stock exchange also known as a securities exchange is a trading platform. It facilitates the registered stockbrokers and investors, often through a stock trading app, to transact in securities electronically. India has two premier stock exchanges include National Stock Exchange (NSE) and the and BSE Limited (BSE).
3. Companies
Every share that you see available to be purchased or sold in the stock market today are those issued by publicly traded companies. When a company makes an Initial Public Offer (IPO), it becomes publicly traded, which means it introduces itself in the stock exchange.
Now we come to the most important participant in the stock market — investors and traders such as you.
4. Investors and traders
You may know that trading and investing are two very different activities. But when you invest in a publicly listed company in the stock exchange, you are regarded as an investor.
On the other hand, if you are looking to buy into a security for a short-term horizon with the intention of profiting from price fluctuation in a stock, you are regarded as a trader.
In the stock market, traders and investors have different objectives, strategies and modes of approaching financial markets.
Within investors, there are two types. These include:
Retail investors – These are investors who invest in the stock market directly.
Institutional investors – These are typically financial institutions like banks, Asset Management Companies (AMC), insurance companies, pension funds, etc. The investors could be domestic or foreign. We now arrive at the fifth and final stock market participant — market intermediaries.
5. Market intermediaries
Intermediaries are entities that are involved in a financial transaction in the market apart from the buyer and seller. These are institutions that help you carry out your investment activity smoothly while ensuring all the rules laid out by the regulator are met.
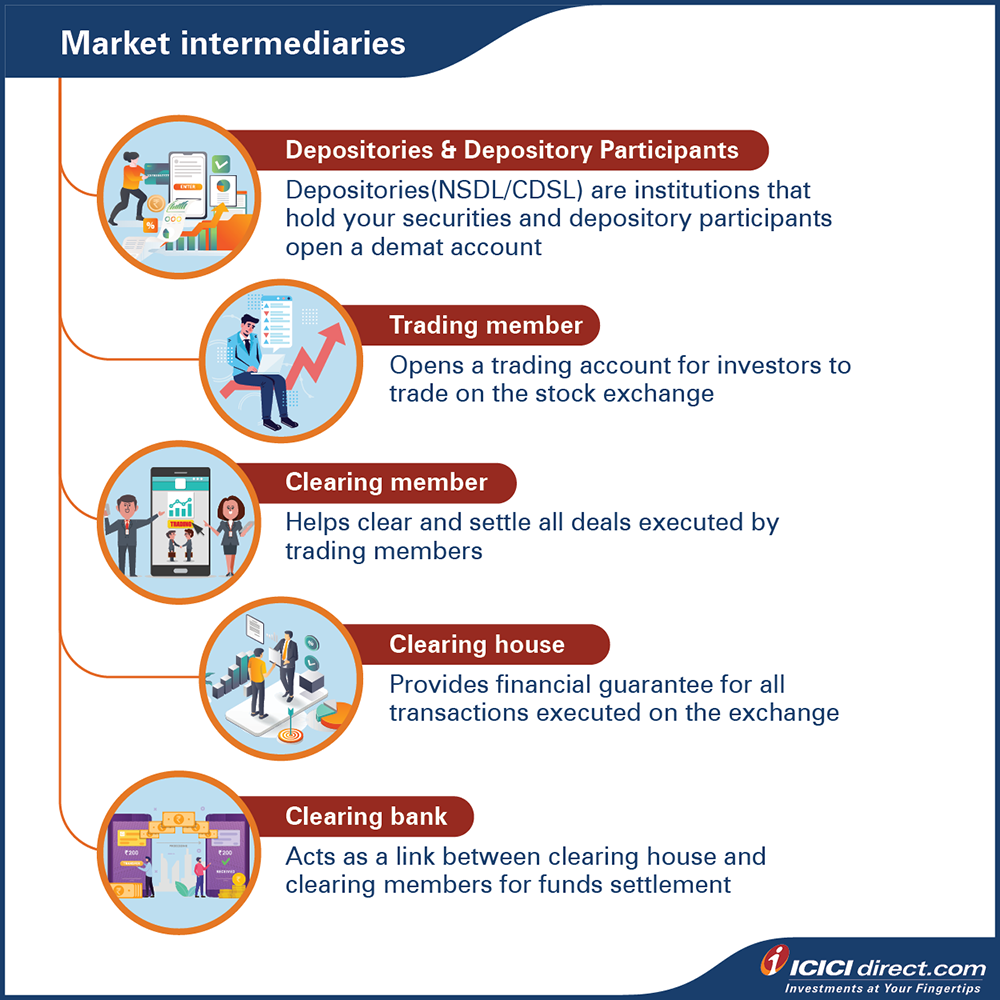
These intermediaries include
- Depositories and Depository Participants (DP) –
In the 90s, if you had to claim ownership of any company you’ve invested in, you had to present a share certificate in a paper format. But in this digital age, the paper format was converted into digital format which is known as Dematerialization or what is commonly known as DEMAT.
This brings us to the role of depositories. They are institutions that hold your securities in this digital format. So, in other words, a depository can be conceived of as a ‘bank’ for securities.
In India, there are two such organizations viz. National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL) and Central Depository Services Limited (CDSL). However, you cannot open an account with these depositories directly. You will have to reach out to an agent, also known as Depository Participant (DP) to provide you with an account.
- Trading member –
A trading member or a stock broker is a member of a stock exchange and can provide securities trading facilities to investors.
They can be individuals (sole proprietors), partnership firms, corporates and banks, who are permitted to become trading members of recognized stock exchanges, subject to fulfillment of eligibility criteria. These members can be associated with multiple stock exchanges to provide trading services to investors.
Since you cannot directly trade on the stock exchange, you need to open a trading account with a stock broker to invest in stock markets.
- Clearing member –
Clearing members are those who help clear and settle all deals executed by trading members through clearing houses.
- Clearing house –
These houses act as a mediator between two entities or parties. They make sure you get the right number of securities at the price you paid for them. This means, they virtually eliminate counter-party risks.
So, basically, a clearing corporation (clearing house) is responsible for clearing and settling all transactions including shares and funds executed in the stock market. It also provides financial guarantee for all transactions executed on the exchange
Did you know?
NSE Clearing Limited (NSE Clearing), a wholly owned subsidiary of National Stock Exchange (NSE) is responsible for clearing and settlement of all trades executed on NSE.
- Clearing bank –
A clearing bank acts as a link between clearing corporations and clearing members. Every clearing member needs to maintain an account with a clearing bank to settling funds and other obligations to the clearing corporations That’s also why it is the responsibility of clearing members to maintain sufficient balance to meet obligations.
Additional Read: Taxation on Equity Investments
Summary
- The five main participants of the stock market include SEBI, which is the regulator, the stock exchanges, publicly listed companies, investors and traders and market intermediaries.
- The Indian stock market is governed by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- There are two premier stock exchanges in India —National Stock Exchange (NSE) and the and BSE Limited (BSE).
- Investors in the stock market are typically of two types — retail investors and institutional investors.
- Market intermediaries consist of Depository Participant (DP), trading members, clearing members, clearing houses and clearing banks.
Now that you've got a good overview of what comprises the stock market, let's get acquainted with the workings of the stock market.

 Top Mutual Funds
Top Mutual Funds





COMMENT (0)