Learning Modules Hide
Hide
- Chapter 1: A Stock Market Guide on Equity Investment
- Chapter 2: Learn Risk & Return on Equity Investment in Detail
- Chapter 3: Learn the Basics of Stock Market Participants and Regulators
- Chapter 4: How Does the Stock Market Work?
- Chapter 5: Guide to stock market trading
- Chapter 6: Stock market investment- Part 1
- Chapter 7: Stock market investment- Part 2
- Chapter 8: What are stock market indices?
- Chapter 9: How to Calculate the Stock Exchange Index: A Stock Market Course for Beginners
- Chapter 10: IPO investing basics
- Chapter 11: Types of IPO Investors in Stock Market
- Chapter 12: IPO Process- From Merchant Banker to Company Listing
- Chapter 13: IPO investment and FPO
- Chapter 14: Important things and Advantages of IPO Investment
- Chapter 15: Corporate Actions: Meaning, Types & Examples
- Chapter 16: Bonus Issue and Rights Issue
- Chapter 17: Corporate Action Purpose and Participation Method
- Chapter 1: Stock Market Valuation- Tips and Techniques
- Chapter 2: Stock Market Valuation- Important Ratios and Terms
- Chapter 3: Types of Stocks in Share Market- Part 1
- Chapter 4 –Types of Stocks in Share Market- Part 2
- Chapter 5: Taxation on Stock Investments – Part 1
- Chapter 6 – Taxation on Stock Investments – Part 2
- Chapter 7 - Difference Between Micro & Macro Economics
- Chapter 8 – Inflation and its Impact on the Economy
- Chapter 9 - Introduction to Economic Policies – Part 1
- Chapter 10 – Introduction to Economic Policies – Part 2
- Chapter 11 – GDP and the Government Budget
- Chapter 12 – Introduction to Foreign Investments and Business Cycles
- Chapter 13 - Economic Indicators
- Chapter 14 - Behavioural Biases and Common Pitfalls in Investment – Part 1
- Chapter 15 - Behavioural Biases and Common Pitfalls in Investment – Part 2
- Chapter 16 - Behavioural Biases and Common Pitfalls in Investment – Part 3
Chapter 7 - Difference Between Micro & Macro Economics
You marvel at the incredible pictures that your friend took of his recent Switzerland tour. In the background in one of his skiing tours you notice a familiar peak.
You squint hard at the image and wonder if it's the famous Alpine Matterhorn.
It appears familiar, and so to get a closer look, what do you do?
That’s right. You ZOOM IN.
And when you want to view the picture in its entirety, you obviously ZOOM OUT.
So, in economics… wait, what’s that now? Why study economics?
That’s because studying economics may help you understand the potential ramifications of economic policies on various industries. It is a tool that may help you predict macroeconomic conditions and realise the implications of those predictions on businesses, stocks, and financial markets.
Now, when it comes to studying economics of a country, the ZOOMED-IN version is called as microeconomics and the ZOOMED-OUT version is called as macroeconomics.
Now, let’s understand what they are.
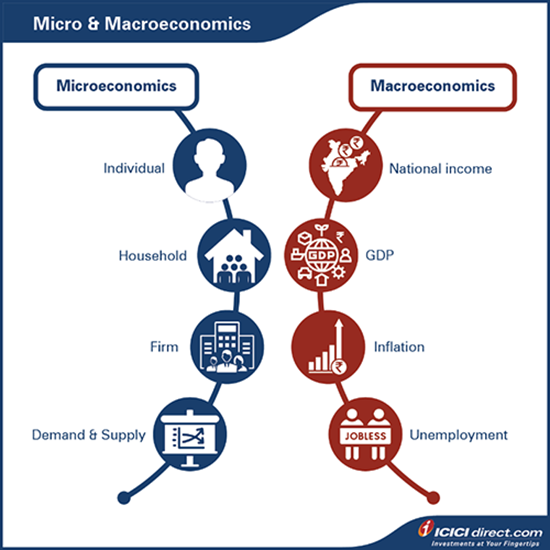
Microeconomics
Microeconomics focuses on the study of decisions taken by individuals, businesses, households, workers and so on.
Let’s understand this with an example:
Say, you have been driving your car to work every day. But of late, the increasing price of petrol has begun to worry you.
You wonder if carpooling may be a good idea. You speak to a couple of your colleagues living in your vicinity. And they gladly welcome your idea of carpooling.
The decision of carpooling was made and agreed due to the exponential patrol price hike.
The study of how specific changes in commodity prices can lead to an individual or business changing their action is known as microeconomics.
Did you know?
The term ‘micro’ comes from Greek word ‘mikrós’ which means ‘small’.
Macroeconomics
Microeconomics, on the other hand, deals with issues like inflation, growth, inter-country trades, unemployment and so on.
Did you know?
The term ‘macro’ comes from Greek word ‘makrós’ which means ‘large’.
Microeconomics and macroeconomics are complementary to each other.
Microeconomics is similar to a bottom-up approach, where individuals and businesses are first analyzed followed by an industry and eventually the country.
Macroeconomics is more like a top-down approach, where the country is first analyzed, subsequently the industry and finally individuals or businesses. Macroeconomics factors play a vital role on stock market growth and performance.
What are the factors that macroeconomics concentrates on?
Well, it focusses more on factors such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP), unemployment rate, inflation, interest rate, government debt, business cycles and so on.
But how does this affect the stock market?
Let’s summarize the impact of these factors with the following table:
|
Economic factors |
Impact on Equity |
|
Rise in inflation |
Bad |
|
Rise in GDP |
Good |
|
Rise in unemployment rate |
Bad |
|
Rise in interest rate |
Bad |
|
Rise in government debt |
Bad |
|
Business cycles - Boom phase and recovery phase |
Good |
Also Read: Chapter 10: Economics for Stock Market
Summary
- Microeconomics focuses on the study of decisions taken by individuals, businesses, households, workers and so on.
- Macroeconomics focuses on issues like inflation, growth, inter-country trades, and so on.
In the following chapters, we will cover the mentioned economic factors and how they impact the equity market.

 Top Mutual Funds
Top Mutual Funds





COMMENT (0)