Understand Everything About Dividend Yield- Meaning, Uses & Examples
Dividend yield is a financial ratio that shows the percentage of a company’s annual dividend payments relative to its stock price. It's commonly used by investors to gauge how much income they can expect to receive from owning a stock, expressed as a percentage.
What Is the Dividend Yield?
The dividend yield is the annual dividend amount paid by a company divided by its current stock price. It's an important metric for income-focused investors, as it measures the return in dividends they get on their investment, excluding any potential capital gains from price appreciation. For instance, if a stock is trading at Rs 100, and the annual dividend is RS 5 per share, the dividend yield would be 5%. A higher dividend yield suggests higher income from the investment but could also signal potential risks or challenges within the company. It is crucial to examine dividend yield alongside other factors to assess a stock’s overall appeal.
How to Calculate Dividend Yield
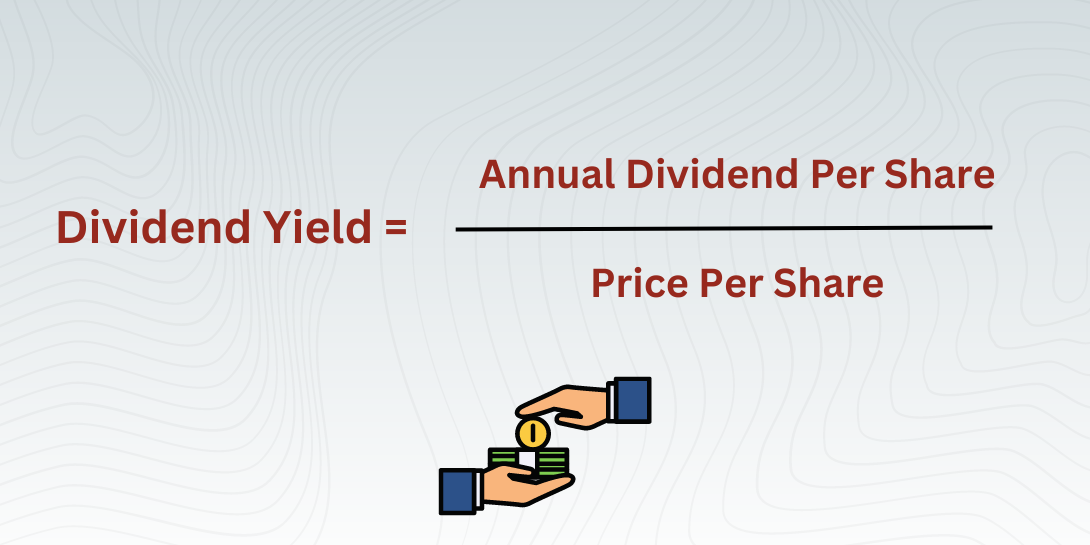
The formula for calculating the dividend yield is:
Dividend Yield = (Annual Dividends Per Share ÷ Price Per Share) × 100
This formula provides a percentage that indicates how much income an investor receives relative to the stock's price. For example, if a company pays Rs 2 per share in dividends annually and its stock is priced at Rs 50, the dividend yield is 4%. However, investors must be cautious, as a high dividend yield may not always mean a better investment. It could indicate that the stock price has dropped due to underlying issues in the company.
What Affects Dividend Yield?
|
Factor |
Impact on Dividend Yield |
|
Stock Price Fluctuations |
As the stock price decreases, the dividend yield increases and vice versa. |
|
Company Dividend Policy |
Changes in the company's dividend policy directly affect the yield. |
|
Earnings Growth |
Strong earnings growth can lead to higher dividends, boosting yield. |
The dividend yield is influenced by various factors, with the stock price being the primary determinant. When the stock price falls, the dividend yield tends to rise, even if the dividend amount remains constant. Conversely, if the stock price increases, the dividend yield may decrease. Additionally, the company's dividend policy plays a crucial role—companies with consistent dividend increases usually attract yield-seeking investors. Earnings growth also impacts dividend yield as companies with rising profits tend to distribute higher dividends.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Dividend Yield
Advantages of Dividend Yield
- Regular income source for investors.
- Attracts conservative investors looking for stability.
- Offers a benchmark for comparing stocks.
Disadvantages of Dividend Yield
- High yield may indicate financial distress.
- Low dividend growth potential may limit overall returns.
- Does not account for stock price depreciation.
Dividend yield serves as an indicator of steady income, attracting conservative and income-focused investors. However, relying solely on dividend yield can be misleading, as a very high yield may signal financial troubles in the company. Investors need to strike a balance between dividend income and stock price appreciation to maximize their returns.
Dividend Yield vs. Dividend Payout Ratio
|
Metric |
Definition |
|
Dividend Yield |
Percentage of a company's price paid in dividends |
|
Dividend Payout Ratio |
The percentage of earnings paid out as dividends |
While the dividend yield measures the return an investor receives in dividends relative to the stock price, the dividend payout ratio shows how much of a company's earnings are being paid out as dividends. A high dividend yield may not always indicate sustainability, but a low payout ratio suggests the company is retaining earnings for future growth.
Dividend Yields and Inflation
Inflation can erode the purchasing power of dividends, reducing their real value over time. As inflation rises, the fixed income from dividends may not keep pace, leading to a decrease in the investor's overall returns. Some companies may increase their dividends to combat inflation, but this is not always guaranteed. Investors should consider inflation when evaluating the true income provided by dividend-paying stocks. Ideally, companies that have a history of increasing dividends regularly can help protect against inflationary pressures.
Examples of Dividend Yield
Consider the case of a utility company with a stock price of Rs 50 and an annual dividend of Rs 3 per share. The dividend yield would be 6%. Another example is a technology firm that pays an annual dividend of Rs 1 per share with a stock price of Rs 200, resulting in a yield of only 0.5%. These examples show that high dividend yields are more common in mature industries like utilities, while growth sectors like technology often focus on reinvesting profits rather than paying large dividends. Both types of companies serve different investor needs depending on whether they prioritize income or growth.
What Does the Dividend Yield Tell You?
Dividend yield tells investors how much they can expect to earn in dividends relative to the stock price. A high yield can be attractive, signalling strong income potential. However, it can also indicate that the stock price has fallen, possibly due to company-specific issues. On the other hand, a low yield may suggest that the company is reinvesting earnings into growth opportunities. Therefore, it's essential to consider the dividend yield within the broader context of the company's financial health.
Why Is Dividend Yield Important?
- Regular Income: Dividends provide a consistent cash flow, which can be especially valuable during market downturns.
- Income Generation: Investors can use dividends to supplement their income or reinvest them for further growth.
- Company Health: A high dividend yield often indicates a financially stable company with strong cash flow.
- Investor Confidence: Companies that consistently pay dividends often instil confidence in investors.
- Dividend Growth: Some companies increase their dividends over time, providing long-term income growth.
Is a High Dividend Yield Good?
A high dividend yield may seem attractive to investors seeking income, but it can also be a red flag. In some cases, a high yield is the result of a declining stock price, which could indicate underlying issues within the company. Therefore, while a high yield can boost returns, it’s essential to evaluate the sustainability of the dividend and the company’s financial stability before making an investment decision.
Which Stock Has the Highest Dividend Yield?
Stocks in the real estate, energy, and utilities sectors often offer the highest dividend yields. For example, real estate investment trusts (REITs) and energy companies are known for paying high dividends to investors. However, it's essential to look beyond the yield and assess the long-term sustainability of those dividends.
Conclusion
Dividend yield is a vital metric for income-focused investors, providing a snapshot of the return they can expect in the form of dividends relative to the stock price. While a high dividend yield may be enticing, it is crucial to analyse the company’s overall financial health and growth prospects to ensure that the dividend is sustainable. Investors should strike a balance between dividend income and the potential for capital gains to achieve the best possible return on their investments.
 Top Mutual Funds
Top Mutual Funds







COMMENT (0)